- Electrical Conductivity -
Used to identify the presence and measure the amount of soluble salts in building materials based on their response to electric conductivity.
dating
morphology
technology
origin
composition
alteration
Ceramic

Mortar

Stone
Stone, Mortar & Plaster, Ceramic Building Materials (CBM)
EC tests are performed in order to monitor both surface and internal soluble salts, to quantify their concentration in a specimen, to test the “state of health” of a building material before salt reduction/extraction treatments, to locate possible humidity sources (which will present higher soluble salt concentrations) and to test the resistance to saline attack of replacement materials in the laboratory prior to their use.
Electrical conductivity test diagram
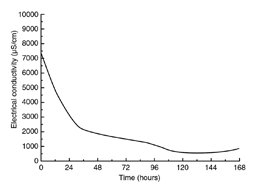
Electrical conductivity tests are used in order to map the presence and distribution of soluble salts, as well as to quantify them in a material. EC does not identify the nature of those salts, but can be used to measure their concentration in a given material. Produces graphs depicting the salinity percentage of the sample.
accuracy
time
cost
in situ
invasive
destructive
Electrical conductivity (EC) refers to the ability of a material to conduct an electric current. Electrical conductivity increases proportionally to the concentration of soluble salts. However, not all salts are equally soluble in H2O. To perform EC tests an alternating current source produces an electric current which flows from one electrode to the other, through the specimen or through the salt-bearing water solution of a sample which has previously been immersed in distilled water. A temperature sensor collects temperature measurements and a converter transforms electrical conductivity into salt content data.