Measures the porosity and studies the pore properties of materials by means of injection of Mercury or Nitrogen.
dating
morphology
technology
origin
composition
alteration

Mortar

Stone
Mortar & Plaster
Mortars and plasters are subjected to Porosimetry examination in order to determine their porosity parameters, to monitor their susceptibility to weathering, to compare similar masonry materials to each other and to evaluate them.
Stone
Pore morphology and pore size distribution in association with other environmental factors, like humidity and temperature, influence the transport of liquid within stones and salt crystallization. In microporous rocks (pore diameter < 2 nm) salt crystallization is not as high as in macroporous materials (pore diameter >50 nm). Mercury Injection Porosimetry is a routine procedure used on stone materials in order to study their physical properties and to evaluate desalination and consolidation treatments.
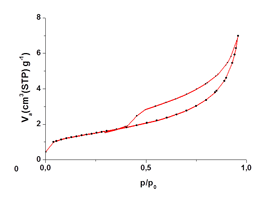
Nitrogen Adsorption Porosimetry graph. Image by Nora Pérez Castellanos.
Porosimetry is an analytical technique used to study the physical properties of porous solids, such as pore diameter, pore volume, surface area, pore size distribution and density. The porosity of a material affects not only its physical behaviour, but also its durability and decay rate. Thus porosimetry is frequently employed for the characterization and classification and the study of the deterioration behaviour of building materials, like masonry, decorative stone or ceramic objects, etc. Prduces a graph featuring pore diameter as a function of volume.
There are two diffused types of Porosimetry:
accuracy
time
cost
in situ
invasive
destructive
First of all, the sample is placed in a sealed penetrometer in order to evacuate air and moisture. Then, by means of a porosimeter, a non-wetting liquid (Mercury, Hg, in the case of MIP) or a gas (Nitrogen, N, in the case of NAP) is forced to intrude into the pores of the specimen at controlled external pressure. Porosimetry is based on the relationship between the external pressure and the volume of the intruded liquid/gas. The volume of Hg/N at the applied pressure gives the volume of all open pores of different radii.